Texas winters can be unpredictable. One day it’s mild, the next you’re waking up to frost. Especially in areas like Van Zandt County, where temperatures drop but rarely stay freezing, deciding between a heat pump or furnace is about finding the right balance between energy efficiency, cost, and comfort. If you’re building or upgrading your Texas home, it’s important to understand how each heating system performs in our climate.
Heat Pump vs Furnace Guide for Texas Homeowners
This guide compares heat pumps and furnaces, breaks down how they work, and weighs the pros and cons to help you determine which system is best for your needs.
Understanding Winter Heating Needs in Texas
Winters in Texas are usually short and mild, especially in towns like Fruitvale and surrounding East Texas. Temperatures may drop, but rarely demand the same heating capacity as colder northern states. That makes heat pumps, which transfer heat rather than generate it, an ideal solution for most homes in the region.
Rather than relying on high-BTU gas furnaces, many Texas homeowners benefit more from heat pumps that offer both heating and cooling while keeping utility costs manageable.
What Is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is a dual-purpose heating and cooling system that can extract heat from the outside air and move it indoors during winter. In summer, it works in reverse to cool your home. This heat exchange process makes it efficient in areas with milder winters, like Texas.
Common Types of Heat Pumps
- Air-source heat pumps – Most popular in Texas due to high energy efficiency and ability to transfer heat instead of generating it.
- Ductless mini-splits – Great for additions or homes without existing ductwork.
- Hybrid systems – Combine a heat pump and a furnace for flexible, reliable heat in any condition.
Unlike a gas furnace, a well-maintained heat pump uses electricity to produce heat and doesn’t rely on natural gas, making it safer and often cheaper to operate.
What Is a Furnace?
A furnace generates and distributes warm air through ductwork by creating heat using natural gas, electricity, or propane. Gas furnaces are common in colder regions but may be more than necessary in a Texas home.
Furnace Fuel Options
- Natural gas – Efficient and lower operating cost when gas lines are available.
- Electric furnace – Useful in rural areas but typically more expensive to operate.
- Propane – A fallback where natural gas isn’t accessible.
While furnaces tend to last longer than heat pumps, they lack the ability to cool your home, requiring a separate air conditioning unit.
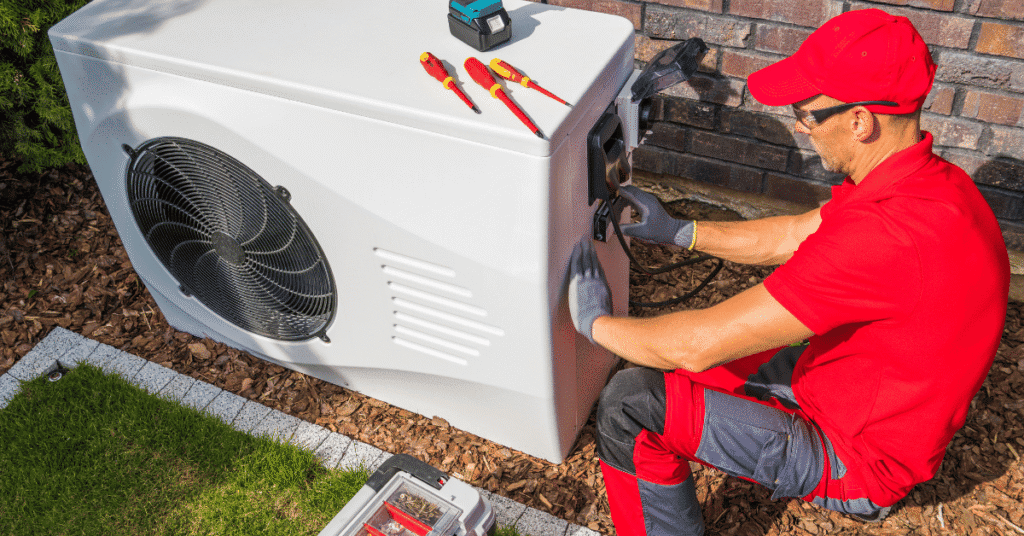
Comparing Heat Pumps and Furnaces for Texas Homes
Choosing between a furnace or a heat pump involves evaluating performance, cost, and climate suitability.
| Feature | Heat Pump | Furnace |
| Heating & Cooling | Yes | No |
| Best Climate | Mild winters (like Texas) | Cold climates |
| Energy Efficiency | High in moderate temperatures | Lower, depends on fuel usage |
| Upfront Cost | Medium to High | Medium |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years | 15–20 years |
| Indoor Air Quality | No combustion, cleaner air | Combustion may emit gases |
Benefits of Heat Pumps
- Provide heating and cooling in one system
- Better energy efficiency in Texas winters
- No combustion means cleaner operation
- Lower monthly bills in milder climates
- Safer to use (no carbon monoxide risk)
Cons of Heat Pumps
- Less effective below 30°F
- Higher installation costs than furnaces
- May need backup heat source during extreme cold
- Performance can drop in long cold snaps
Pros of Furnaces
- Provide consistent heat even in very cold weather
- Often lower initial cost compared to install a heat pump
- Longer lifespan with proper repair and cleaning
Cons of Furnaces
- Require separate air conditioning system
- Can burn more fuel than needed in milder winters
- Higher winter energy bills in Texas
- Less environmentally friendly due to natural gas or propane use

Cost Consideration for Texas Homeowners
Installation Costs
- Heat pump systems: $6,000–$12,000
- Furnace systems: $3,000–$7,000
Monthly Operating Costs
- Heat pumps offer lower electricity use, ideal for moderate Texas winters
- Gas furnaces may cost more per month, especially if used heavily
Maintenance Needs
- Heat pump: Regular coil cleaning, refrigerant checks
- Furnace: Annual safety inspections, repair, and filter changes
Which Heating System Is Best for Your Texas Home?
At All Seasons Professionals, we help Texas homeowners decide between a furnace and a heat pump based on insulation, size, and energy goals.
We Recommend Heat Pumps For:
- Homeowners wanting both heating and cooling
- Well-insulated or smaller homes
- Those focused on energy efficiency
- Clients looking for fewer carbon emissions
We Recommend Furnaces For:
- Larger homes or buildings with high heating demand
- Homes in colder Texas zones with freezing nights
- Properties where natural gas is cheap and available
- Anyone needing backup heat source
Answering Common Client Questions
Can I use both systems together?
Yes, a hybrid system with a heat pump and a furnace offers the best of both worlds. Use the heat pump during mild weather and switch to the furnace during cold snaps.
Are ductless heat pumps good for additions?
Definitely. They’re easy to install, don’t need ductwork, and are efficient for small spaces.
How often do I need service?
Whether you use a furnace or heat pump, get annual checkups, especially before peak winter or summer seasons.
Final Thoughts
Both furnaces and heat pumps have their strengths. For most Texas homes, especially in areas with milder winters, a heat pump is often the best HVAC choice due to its dual-purpose function, safety, and energy efficiency. That said, a gas furnace remains a solid pick for those needing reliable heat during longer cold spells or who already have natural gas access.
If you’re unsure which heating system is best, reach out to the All Seasons Professionals team. We’ll help you find the best system to heat or cool your home, tailored to your property and budget.




